Emerging Trends in Transportation
Advancements in technology continue to reshape how we think about travel. Key trends like autonomous vehicles and the electrification of transport are at the forefront of this transformation.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars, offer transformative potential for transportation. Companies like:
- Tesla
- Waymo
- Uber
are developing advanced autonomous systems to improve road safety and efficiency.
With capabilities such as real-time data processing and machine learning, these vehicles can make split-second decisions to avoid accidents.
By 2030, it’s estimated that 30% of new cars will have some level of autonomous functionality, reducing human error, which accounts for 94% of accidents according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
Electrification of Transport
The shift to electric vehicles (EVs) aims to reduce carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Leading automakers such as Tesla, Nissan, and General Motors are investing heavily in electric technology.
As battery technology advances, EVs now offer longer ranges and faster charging times. BloombergNEF forecasts that by 2040, 58% of global passenger vehicle sales will be electric.
Electric buses and trucks are also gaining traction, providing sustainable options for public transport and logistics, further reducing the carbon footprint.
Innovations in Public Transit Systems
Public transit systems are evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and a push for sustainability. The future promises faster, greener, and more efficient public transportation options.
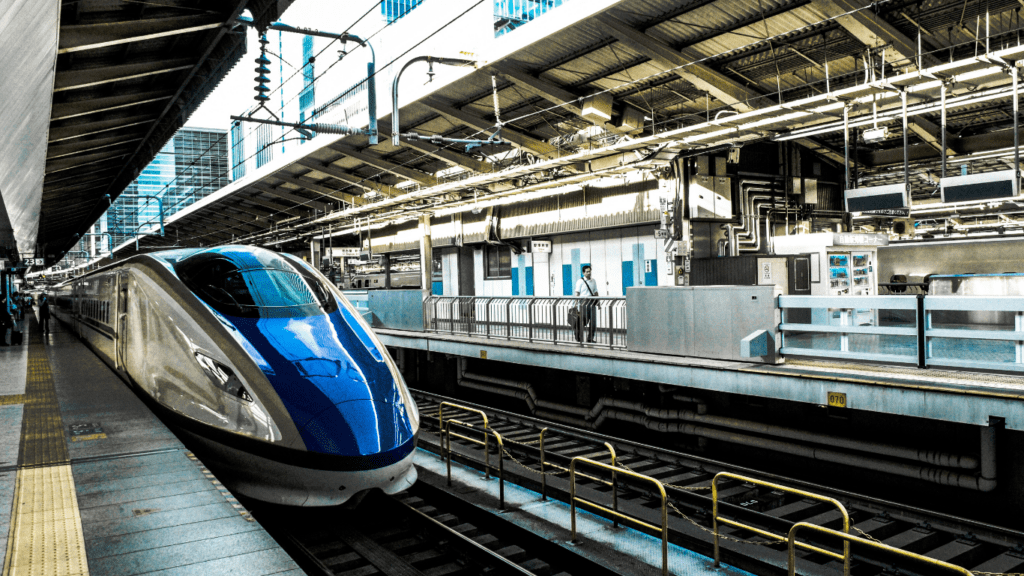
Hyperloop and High-Speed Trains
Hyperloop technology is spearheading efforts to revolutionize travel. Companies like Virgin Hyperloop and Elon Musk’s The Boring Company are developing systems capable of transporting passengers at speeds exceeding 700 mph.
This technology uses vacuum tubes to minimize air resistance and friction, reducing travel times significantly. For instance, a trip from Los Angeles to San Francisco could take under 30 minutes using a hyperloop, compared to 6 hours by car.
High-speed trains in countries like Japan, France, and China have set benchmarks for efficient rail travel. Japan’s Shinkansen, running at speeds up to 200 mph, serves as a model of punctuality and safety.
China’s CR400 Fuxing series, operating at similar speeds, connects major cities across vast distances, making rail travel a feasible alternative to air travel.
Green Urban Mobility Solutions
Green urban mobility solutions are gaining traction as cities aim to reduce carbon footprints.
Electrification of buses, trams, and trolleys is critical. Cities like Oslo and Shenzhen are leading the way by implementing all-electric bus fleets. Oslo has committed to a zero-emission public transportation system by 2028.
Bicycle-sharing programs and electric scooters are transforming short-distance travel. Programs in cities like Amsterdam and Copenhagen exemplify the integration of cycling into urban transport infrastructure.
Electric scooters, deployed in cities like San Francisco and Washington D.C., provide convenient last-mile connectivity.
Advanced traffic management systems use AI to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. Smart traffic lights, adaptive signaling, and real-time data collection improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
Singapore’s Intelligent Transport System (ITS) efficiently manages traffic through such innovations.
Public transit systems of the future focus on speed, efficiency, and sustainability, promising to transform urban landscapes while addressing environmental concerns.
Impact of Technology on Transportation

Technological advancements are reshaping transportation systems globally. Emerging technologies like AI and mapping solutions promise efficiency and safety.
AI and Machine Learning Applications
- AI and machine learning optimize transportation systems. Self-driving cars, for instance, predict traffic patterns and adjust routes.
- In 2021, 34 cities worldwide tested autonomous buses to reduce human error (McKinsey & Company).
- AI also enhances logistics by predicting delivery times and optimizing supply chains.
- Urban planners use AI to design smart cities, integrating data from various sources to improve public transit routes.
- Companies like Google and Amazon use machine learning for predictive maintenance of vehicles, reducing downtime.
Advancements in GPS and Mapping Technologies
GPS and mapping technologies now offer precise real-time data. Advanced GPS systems integrate with AI to provide accurate traffic predictions.
Waymo’s autonomous vehicles combine GPS with 3D mapping to navigate complex urban environments safely. Updated mapping technologies aid emergency services by providing the fastest routes in real-time.
According to Statista, the GPS tracking market is projected to grow from $2.53 billion in 2020 to $4.15 billion by 2025. These advancements make navigating cities and planning long-distance travel more efficient and reliable.
Environmental Considerations in Future Transportation
New transportation technologies promise massive impacts on our environment.
Reduction in Carbon Emissions
Electric vehicles (EVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly lowering air pollution. Companies like Tesla and Nissan invest heavily in EV development.
According to the International Energy Agency, global EV stock surpassed 10 million in 2020. Adoption of EVs by 2040 is expected to cut carbon emissions by 1.5 gigatons annually.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles use hydrogen gas, emitting only water vapor. Toyota’s Mirai and Hyundai’s Nexo exemplify this technology. Green hydrogen production can further reduce emissions, supported by renewable energy sources.
Sustainability in Transportation Design
Sustainable materials and designs improve transportation’s environmental footprint. Manufacturing processes use recycled materials, decreasing waste and energy consumption. For instance, Ford uses recycled plastics for vehicle parts.
Green architecture integrates into public transit systems. Solar panels on bus stops and train stations reduce energy usage. Beijing’s Daxing Airport, designed with eco-friendly concepts, incorporates natural lighting and solar energy.
Overall, these advancements in reducing carbon emissions and sustainable design reflect a clear pathway toward eco-friendly transportation systems.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Riley Ireland
Riley Ireland is a dedicated contributor and article writer at The Global Reach Visionary, where her expertise in international marketing and global business strategies adds valuable depth to the platform. With a strong background in global commerce and a keen eye for emerging market trends, Riley has a talent for breaking down complex economic shifts into insightful, accessible content. Her passion for exploring the intricacies of international trade and business dynamics allows her to provide readers with actionable knowledge, helping them navigate the ever-changing global landscape with confidence and clarity.